Your home should be a place of comfort and safety, but hidden dangers can lurk where you least expect them. One such threat is radon, a radioactive gas that can accumulate indoors without any taste, color, or smell. Understanding the science behind radon gas helps homeowners protect their households from its effects. Learn what radon gas is, why it’s harmful, and how to protect your home.
Where Radon Comes From
Radon is a radioactive gas that forms naturally when uranium in soil, rock, and water breaks down. As uranium decays, it releases radon, which rises through the ground and into the air. This process occurs everywhere, so any home could potentially have high radon levels.
Because it is a gas, radon can easily travel through small spaces and accumulate in enclosed areas such as basements and crawl spaces. The concentration of radon can vary significantly from one home to another, even within the same neighborhood, depending on local geology and home construction.
How Radon Enters Your Home
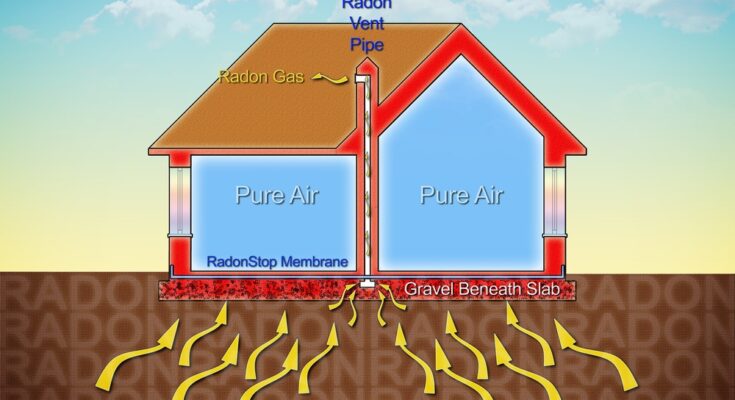
Radon gas can seep into your home through various entry points, typically in the lowest levels of the structure. Cracks in concrete slabs, basement floors, and foundation walls are common pathways for radon to enter. Gaps around service pipes, construction joints, and sump pump pits also provide openings for the gas.
The air pressure inside a home is often lower than the pressure in the soil around the foundation, creating a vacuum effect that pulls radon gas indoors. One reason radon is a greater risk at higher elevations is lower atmospheric pressure, which can amplify this effect and draw more radon into the home. Once inside, the gas can become trapped and reach dangerous concentrations.
Why Radon Is a Health Concern
Long-term exposure to radon is a serious health risk and is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States, surpassed only by smoking. When you breathe in radon, its radioactive particles enter the lungs and break down, releasing energy that can damage lung tissue.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) advises that there is no known safe level of radon exposure, meaning any amount carries some degree of risk. The danger is particularly high for certain groups who are more susceptible to its effects, including children and individuals with respiratory conditions.
How to Detect and Mitigate Radon Levels
Radon is undetectable by human senses, but professional home radon testing services protect families. Testing provides the most accurate and reliable results, using specialized equipment to measure radon concentrations over a specific period.
If testing reveals high radon levels, a professional mitigation system can be installed to reduce concentrations. These systems create a suction point beneath the home’s foundation and use a fan to draw radon gas out from under the house and vent it safely outdoors.
Radon may be an invisible threat, but its risks are well-documented and entirely manageable with the right knowledge and tools. Understanding the science behind radon empowers homeowners to protect themselves and their loved ones. Investing in professional radon testing and mitigation is a simple, effective way to improve your home’s air quality.